Tijauan Mekanisme Koping dan Strategi Pertahanan Diri Siswa Korban Perundungan di Lingkungan Sekolah
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61815/alibrah.v10i2.769Keywords:
Bullying, Psychology,, Education, SchoolAbstract
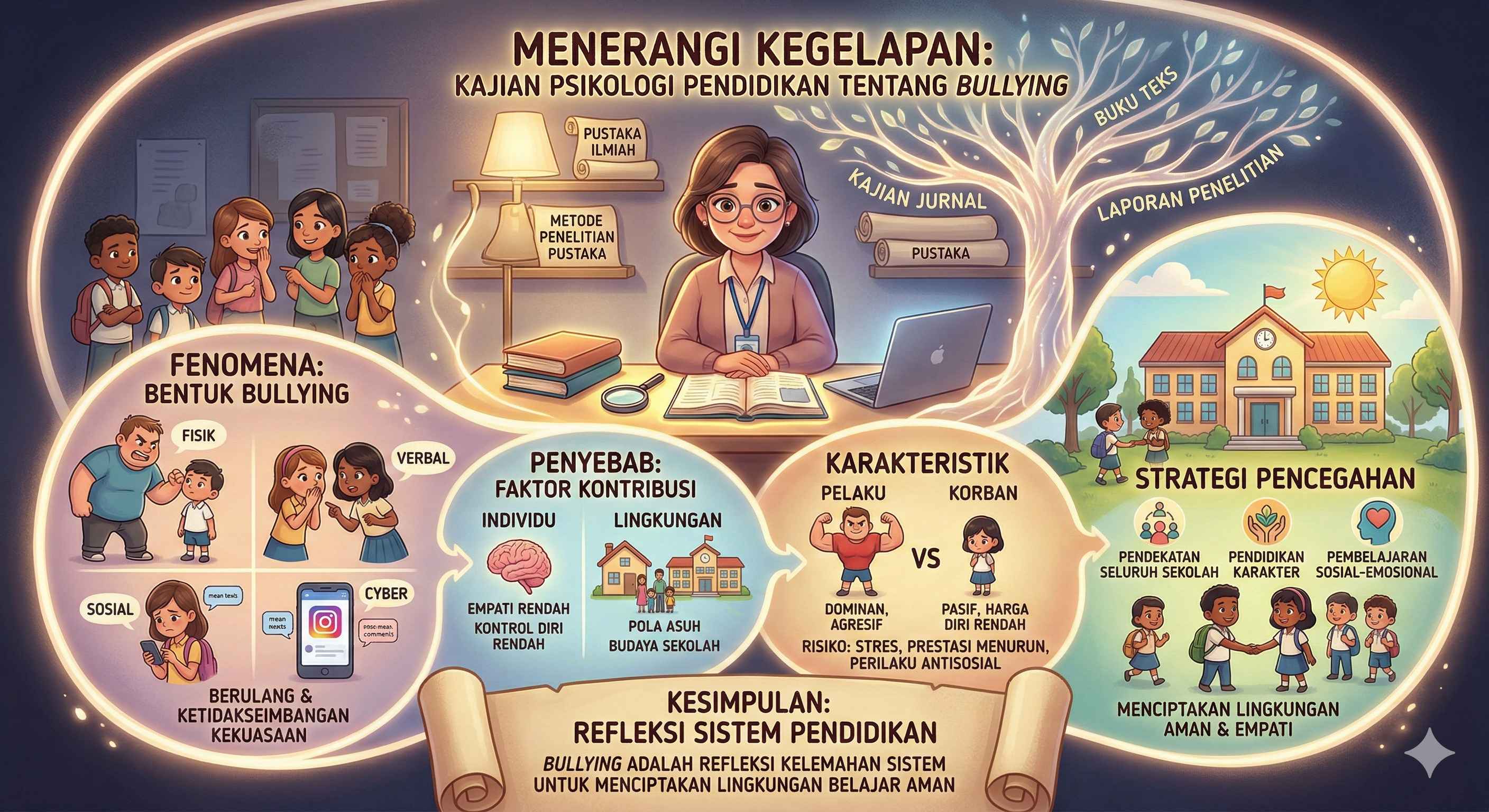
This study aims to examine the phenomenon of bullying in schools from an educational psychology perspective using the library research method. This study reviews various scientific sources, such as journals, books, and research reports, to understand the forms, causes, characteristics of perpetrators and victims, impacts, and strategies for preventing bullying in educational settings. The results of the study show that bullying includes physical, verbal, social, and cyber forms that are repetitive and accompanied by an imbalance of power. The contributing factors include individual aspects, such as low empathy and self-control, as well as environmental factors, such as parenting patterns and school culture. Perpetrators generally exhibit dominant and aggressive traits, while victims tend to be passive and have low self-esteem. The impacts include psychological distress, decreased academic performance, and the risk of antisocial behavior. Effective strategies to address bullying include a whole-school approach, character education, and social-emotional learning. This study emphasizes that bullying is not only an individual behavioral problem but also a reflection of the weakness of the education system in creating a safe and empathetic learning environment.
Downloads
References
Aidar. (2025). Bullying Dalam Perspektif Psikologi Pendidikan. Jurnal Pendidikan, Riset Dan Teknologi, 1(1), 39–49.
Campbell, M., & Bauman, S. (2018). Cyberbullying: Definition, consequences, prevalence. In Reducing Cyberbullying in Schools. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811423-0.00001-8
Gage, N. A., Prykanowski, D. A., & Larson, A. (2014). School Climate and Bullying Victimization : A Latent Class Growth Model Analysis. Scool Psychology Quarterly, 29(3), 256–271.
Hidayat, M. T. (2022). Strategi Guru dalam Mengatasi Perilaku Bullying Siswa di Sekolah Dasar Ramadhanti Jurnal Basicedu, 6(3), 4566–4573.
Hinduja, S., & W.Patchin, J. (2020). Cyberbullying (2020 (ed.)).
Hymel, S., & Swearer, S. M. (2015). Four Decades of Research on School Bullying. Amrican Psychologist, 70(4), 293–300.
Ifroh, R. H., Dwi, A., Suci, R., & Fajariani, W. (2018). Pemberdayaan siswa sekolah dasar di wilayah kampung kb pelita kencana kelurahan pelita mengenai bullying usia sekolah. 1(3), 184–196.
Jenkins, L. N., & Demaray, M. K. (2015). INDIRECT EFFECTS IN THE PEER VICTIMIZATION-ACADEMIC ACHIEVEMENT RELATION : THE ROLE OF ACADEMIC SELF-CONCEPT AND GENDER. 1.
Juvonen, J., & Graham, S. (2014). Bullying in Schools : The Power of Bullies and the Plight of Victims. 1(10), 160–185. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010213-115030
Kartika, K., Darmayanti, H., & Kurniawati, F. (2020). Sistematik Reviu Strategi Coping yang Diterapkan Korban Face-to-face Bullying dan Cyberbullying. Jurnal Psikologi Integratif, 8, 41–69.
Kowalski, R., Limber, S. P., & Mccord, A. (2018). A Developmental Approach to Cyberbullying : Prevalence and Protective Factors. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2018.02.009
Lazarus, R. S., & Folkman, S. K. (1984). Stress, appraisal, and coping. Springer Publishing Company.
Modecki, K. L., Minchin, J., Harbaugh, G, A., Guerra, N. G., & Runions, K. (2014). Bullying Prevalence Across Contexts : A Meta-analysis Measuring Cyber and Traditional Bullying. Journal of Adolescent Health, 55(5), 602–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2014.06.007
Olweus, D. (2013). School Bullying : Development and Some Important Challenges. 9, 1–30. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185516
Polanin, J. R., Espelage, D. L., Pigott, T. D., Polanin, J. R., Espelage, D. L., A, T. D. P., Polanin, J. R., Espelage, D. L., & Pigott, T. D. (2019). A Meta-Analysis of School-Based Bullying Prevention Programs ’ Effects on Bystander Intervention Behavior A Meta-Analysis of School-Based Bullying Prevention Programs ’ Effects on Bystander Intervention Behavior. School Psychology Review, 41(1), 47–65.
Salmivalli, C., Voeten, M., & Poskiparta, E. (2011). Bystanders Matter : Associations Between Reinforcing , Defending , and the Frequency of Bullying Behavior in Classrooms Bystanders Matter : Associations Between Reinforcing , Defending , and the Frequency of Bullying Behavior in Classrooms. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 40(5), 668–676. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2011.597090
Sari, A. P., Elliya, R., & Triyoso. (2019). HUBUNGAN PERILAKU BULLYING DENGAN TINGKAT STRESS. Jurnal Maternitas Aisyah, 1(1).
Stamland, K., Janne, G., & Hildegunn, S. (2022). Bullying by Teachers Towards Students — a Scoping Review. International Journal of Bullying Prevention. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42380-022-00131-z
Swearer, S. M., & Hymel, S. (2015). Understanding the Psychology of Bullying. 70(4), 344–353.
Ummah, S. Z., Zumrotun, E., & Muhaimin, M. (2025). Dampak Psikologis Bullying terhadap Motivasi dan Prestasi Belajar Siswa di SDN 1 Mindahan. 8(1).
Volk, A. A., Dane, A. V, & Marini, Z. A. (2014). What is bullying ? A theoretical redefinition. Developmental Review, 34(4), 327–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dr.2014.09.001
Zalaluddin, M., Putra, A. S. D., & Salma Haniyah Putri Pernama. (2025). Analisis Masalah Kekerasan Guru Pada Karakter Murid Sekolah Menengah. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan Pancasila Dan Kewarganegaraan, 5(2), 72–78.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 putri Mahirah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.